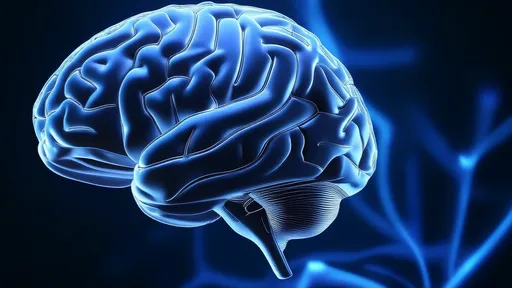
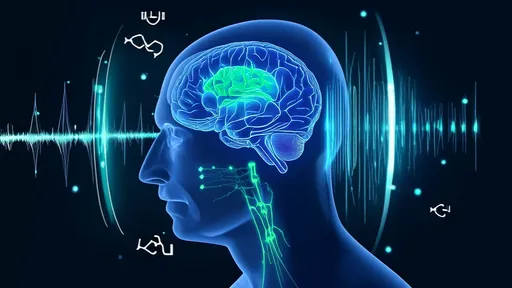
In a groundbreaking development for neural interface technology, researchers have unveiled a revolutionary approach using liquid metal electrodes capable of conforming to the brain's intricate folds. This innovation promises to transform our understanding of brain-computer interfaces by creating seamless, adaptive connections with the cerebral cortex.
The human brain's surface resembles a rugged terrain of hills and valleys, with its characteristic gyri and sulci presenting significant challenges for traditional rigid electrodes. Conventional neural interfaces often struggle to maintain consistent contact with the cortical surface, leading to signal degradation and potential tissue damage. The liquid metal solution elegantly overcomes these limitations through its unique physical properties.
Gallium-based alloys have emerged as the material of choice for these adaptive electrodes. These metals remain liquid at body temperature while exhibiting exceptional conductivity – approximately ten times greater than conventional hydrogel electrodes. When introduced to the brain's surface, the liquid metal spontaneously flows into the sulci, creating perfect topographic correspondence without external pressure.
Professor Elena Vostrikova, lead researcher at the Neurotechnology Institute, explains: "The self-wetting properties of these alloys allow them to 'paint' themselves across the cortical surface, mirroring every contour. What we've achieved is essentially an electronic replica of the brain's folding pattern at the interface level." This intimate contact enables unprecedented signal resolution from both superficial and deep cortical layers simultaneously.
Safety considerations have been paramount in the development process. The gallium-indium-tin alloy demonstrates remarkable biocompatibility, with animal studies showing no signs of inflammatory response or neuronal damage after six months of continuous implantation. The liquid metal remains contained within a microscale elastomer framework that prevents migration while permitting the necessary fluidity for conformation.
Clinical applications appear particularly promising for epilepsy monitoring and brain mapping prior to tumor resection. Neurosurgeons report that the liquid metal electrodes provide significantly clearer localization of seizure foci compared to conventional grid electrodes. The technology's ability to conform without compression also reduces the risk of cortical contusions during prolonged monitoring sessions.
Beyond clinical diagnostics, the innovation opens new possibilities for cognitive research. The electrode arrays can be fabricated with hundreds of micrometer-scale contacts, enabling researchers to map neural activity patterns across entire functional networks with spatial precision previously unattainable. Early experiments have already revealed novel details about information processing in the prefrontal cortex during complex decision-making tasks.
Manufacturing these interfaces requires novel approaches. Researchers employ microfluidic channels filled with liquid metal within stretchable polymer matrices. The resulting devices maintain conductivity even when stretched to 300% of their original size – a critical feature for accommodating brain movement during physiological processes like pulsation or positional changes.
Challenges remain in scaling up production and achieving long-term stability under continuous electrical stimulation. The research team is currently developing protective oxide layers that maintain electrical properties while preventing alloy degradation. Early prototypes have demonstrated stable performance for over 1,000 hours of continuous operation in simulated physiological conditions.
Regulatory pathways for this novel technology are still being established. The FDA has granted breakthrough device designation for the liquid metal electrode system, with first-in-human trials expected to begin within eighteen months. Meanwhile, the team is collaborating with major neurotechnology companies to develop manufacturing standards for clinical-grade devices.
Ethical considerations surrounding brain interface technologies remain at the forefront of discussions. The developers have emphasized that current implementations focus solely on recording neural activity rather than stimulation. A transparent neuroethics framework has been established to guide future applications as the technology evolves.
Looking ahead, researchers speculate about potential extensions of the technology. The liquid metal principle might be adapted for peripheral nerve interfaces or even cardiac mapping. Some envision future iterations incorporating nanoscale sensors directly within the metal matrix, creating "smart" interfaces capable of localized neurotransmitter detection.
As this technology matures, it could fundamentally alter our approach to studying and interacting with the nervous system. The marriage of fluid dynamics and neural engineering represented by these adaptive electrodes may well mark the beginning of a new era in brain-machine interfaces – one where the technology disappears into the biological substrate, creating seamless integration between mind and machine.
The scientific community awaits further validation studies with cautious optimism. If successful, this innovation could provide the missing link for high-fidelity neural interfaces that work in harmony with the brain's natural architecture rather than against it. The implications for both basic neuroscience and clinical applications could prove transformative.
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025

By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025
By /Aug 5, 2025